SQL Database
NuxtHub Database provides a type-safe SQL database powered by Drizzle ORM, supporting PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQLite with smart detection and automatic migrations at build time.
Getting started
Install dependencies
Install Drizzle ORM, Drizzle Kit, and the appropriate driver(s) for the database you are using:
pnpm add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit postgres @electric-sql/pglite
yarn add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit postgres @electric-sql/pglite
npm install drizzle-orm drizzle-kit postgres @electric-sql/pglite
bun add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit postgres @electric-sql/pglite
deno add npm:drizzle-orm drizzle-kit postgres @electric-sql/pglite
npx nypm add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit postgres @electric-sql/pglite
- Uses
PGlite(embedded PostgreSQL) if no environment variables are set. - Uses
postgres-jsdriver if you setDATABASE_URL,POSTGRES_URL, orPOSTGRESQL_URLenvironment variable.
pnpm add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit mysql2
yarn add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit mysql2
npm install drizzle-orm drizzle-kit mysql2
bun add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit mysql2
deno add npm:drizzle-orm drizzle-kit mysql2
npx nypm add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit mysql2
- Uses
mysql2driver if you setDATABASE_URLorMYSQL_URLenvironment variable. - Requires environment variable (no local fallback)
pnpm add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit @libsql/client
yarn add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit @libsql/client
npm install drizzle-orm drizzle-kit @libsql/client
bun add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit @libsql/client
deno add npm:drizzle-orm drizzle-kit @libsql/client
npx nypm add drizzle-orm drizzle-kit @libsql/client
- Uses
libsqldriver for Turso if you setTURSO_DATABASE_URLandTURSO_AUTH_TOKENenvironment variables. - Uses
libsqllocally with file at.data/db/sqlite.dbif no environment variables are set.
Set SQL dialect
Enable the database in your nuxt.config.ts by setting the db property to your desired SQL dialect:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
db: 'postgresql'
}
})
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
db: 'mysql'
}
})
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
db: 'sqlite'
}
})
Database schema
Create your database schema with full TypeScript support using Drizzle ORM:
import { pgTable, text, serial, timestamp } from 'drizzle-orm/pg-core'
export const users = pgTable('users', {
id: serial().primaryKey(),
name: text().notNull(),
email: text().notNull().unique(),
password: text().notNull(),
avatar: text().notNull(),
createdAt: timestamp().notNull().defaultNow(),
})
import { mysqlTable, text, serial, timestamp } from 'drizzle-orm/mysql-core'
export const users = mysqlTable('users', {
id: serial().primaryKey(),
name: text().notNull(),
email: text().notNull().unique(),
password: text().notNull(),
avatar: text().notNull(),
createdAt: timestamp().notNull().defaultNow(),
})
import { sqliteTable, text, integer } from 'drizzle-orm/sqlite-core'
export const users = sqliteTable('users', {
id: integer().primaryKey({ autoIncrement: true }),
name: text().notNull(),
email: text().notNull().unique(),
password: text().notNull(),
avatar: text().notNull(),
createdAt: integer({ mode: 'timestamp' }).notNull(),
})
Generate migrations
Generate the database migrations from your schema:
npx nuxt db generate
This creates SQL migration files in server/db/migrations/{dialect}/ which are automatically applied during deployment and development.
db instance from hub:db.npx nuxt db generate to generate the database migrations each time you change your database schema and restart the development server.Schema definition
NuxtHub supports defining the database schema in multiple files and directories, allowing you to organize your schema files in a way that makes sense for your project, but also open the possibility to Nuxt modules to extend the database schema.
Schema files
Database schema can be defined in a single file or in multiple files, these files are scanned and automatically imported following this glob pattern:
server/db/schema.tsserver/db/schema.{dialect}.tsserver/db/schema/*.tsserver/db/schema/*.{dialect}.ts
The merged schema is exported in hub:db:schema or via the schema object in the hub:db namespace:
import * as schema from 'hub:db:schema'
// or
import { schema } from 'hub:db'
.nuxt/hub/db/schema.mjs.Nuxt layers
Database schema is scanned and automatically imported for each Nuxt layer.
This meands that you can also define schema in the layers directory:
layers/cms/server/db/schema.ts
layers/products/server/db/schema/products.ts
Nuxt modules
If you are a Nuxt module developer, you can also extend the database schema by using the hub:db:schema:extend hook:
import { defineNuxtModule, createResolver } from '@nuxt/kit'
export default defineNuxtModule({
setup(options, nuxt) {
const { resolvePath } = createResolver(import.meta.url)
nuxt.hook('hub:db:schema:extend', async ({ dialect, paths }) => {
// Add your module drizzle schema files for the given dialect
// e.g. ./schema/pages.postgresql.ts if hub.db is 'postgresql'
paths.push(await resolvePath(`./schema/pages.${dialect}`))
})
}
})
Sharing types with Vue
Types inferred from your database schema are only available on the server-side by default. To share these types with your Vue application, you can use the shared/ directory which is auto-imported across both server and client.
Create a types file in the shared/types/ directory:
import { users, posts } from 'hub:db:schema'
// Select types (for reading data)
export type User = typeof users.$inferSelect
export type Post = typeof posts.$inferSelect
// Insert types (for creating data)
export type NewUser = typeof users.$inferInsert
export type NewPost = typeof posts.$inferInsert
These types are now auto-imported and available in your Vue components, composables, and API routes:
<script setup lang="ts">
const { data: users } = await useFetch<User[]>('/api/users')
</script>
import { db, schema } from 'hub:db'
export default eventHandler(async (event) => {
const body = await readBody<NewUser>(event)
return await db.insert(schema.users).values(body).returning()
})
Pick and Omit TypeScript's built-in utility types.// User without password for public API responses
export type PublicUser = Omit<User, 'password'>
// Only the fields needed for user creation form
export type UserForm = Pick<NewUser, 'name' | 'email' | 'password'>
Query database
Now that you have your database schema and migrations set up, you can start querying your database.
The hub:db module provides access to the database through a Drizzle ORM instance.
import { db } from 'hub:db'
db is auto-imported on server-side, you can directly use it without importing it from hub:db.SQL Select
import { db, schema } from 'hub:db'
export default eventHandler(async (event) => {
return await db.query.users.findMany()
// or
return await db.select().from(schema.users)
})
SQL Insert
import { db, schema } from 'hub:db'
export default eventHandler(async (event) => {
const { name, email } = await readBody(event)
return await db
.insert(schema.users)
.values({
name,
email,
createdAt: new Date()
})
.returning()
})
SQL Update
import { db, schema } from 'hub:db'
export default eventHandler(async (event) => {
const { id } = getRouterParams(event)
const { name } = await readBody(event)
return await db
.update(schema.users)
.set({ name })
.where(eq(tables.users.id, Number(id)))
.returning()
})
SQL Delete
import { db, schema } from 'hub:db'
export default eventHandler(async (event) => {
const { id } = getRouterParams(event)
const deletedUser = await db
.delete(schema.users)
.where(eq(schema.users.id, Number(id)))
.returning()
if (!deletedUser) {
throw createError({
statusCode: 404,
message: 'User not found'
})
}
return { deleted: true }
})
Database migrations
Database migrations provide version control for your database schema. NuxtHub supports SQL migration files (.sql) and automatically applies them during development and deployment. Making them fully compatible with Drizzle Kit generated migrations.
.<dialect>.sql suffix (e.g., 0001_create-todos.postgresql.sql).Migrations Directories
NuxtHub scans server/db/migrations for migrations in each Nuxt layer.
To scan additional directories, specify them in your config:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
db: {
dialect: 'postgresql',
migrationsDirs: [
'server/db/custom-migrations/'
]
}
}
})
For more control (e.g., in Nuxt modules), use the hub:db:migrations:dirs hook:
import { createResolver, defineNuxtModule } from '@nuxt/kit'
export default defineNuxtModule({
meta: {
name: 'my-auth-module'
},
setup(options, nuxt) {
const { resolve } = createResolver(import.meta.url)
nuxt.hook('hub:db:migrations:dirs', (dirs) => {
dirs.push(resolve('./db-migrations'))
})
}
})
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT NOT NULL
);
.data/db/migrations when you run Nuxt, giving you a consolidated view.Automatic migrations
Migrations are automatically applied when you:
- Start the development server (
npx nuxi dev) - Build the application (
npx nuxi build)
Applied migrations are tracked in the _hub_migrations database table.
Generating migrations
Once you have updates your database schema, you can generate new migrations using the following command:
npx nuxt db generate
This will generate new migrations files in server/db/migrations/{dialect}/ which are automatically applied during development and deployment.
Applying migrations
Once you have generated new migrations, you can apply them using the following command:
npx nuxt db migrate
This will apply the new migrations to your database.
Post-migration queries
_hub_migrations. Ensure they're idempotent.Use the hub:db:queries:paths hook to run additional queries after migrations:
import { createResolver, defineNuxtModule } from '@nuxt/kit'
export default defineNuxtModule({
meta: {
name: 'my-auth-module'
},
setup(options, nuxt) {
const { resolve } = createResolver(import.meta.url)
nuxt.hook('hub:db:queries:paths', (paths, dialect) => {
paths.push(resolve(`./db-queries/seed-admin.${dialect}.sql`))
})
}
})
INSERT OR IGNORE INTO admin_users (id, email, password) VALUES (1, 'admin@nuxt.com', 'admin');
.data/db/queries when you run Nuxt, giving you a consolidated view.Foreign-key constraints
For Cloudflare D1 with Drizzle ORM migrations, replace:
-PRAGMA foreign_keys = OFF;
+PRAGMA defer_foreign_keys = on;
ALTER TABLE ...
-PRAGMA foreign_keys = ON;
+PRAGMA defer_foreign_keys = off;
Database seed
You can populate your database with initial data using Nitro Tasks:
Enable Nitro tasks
export default defineNuxtConfig({
nitro: {
experimental: {
tasks: true
}
}
})
Create a seed task
import { db, schema } from 'hub:db'
export default defineTask({
meta: {
name: 'db:seed',
description: 'Seed database with initial data'
},
async run() {
console.log('Seeding database...')
const users = [
{
name: 'John Doe',
email: 'john@example.com',
password: 'hashed_password',
avatar: 'https://i.pravatar.cc/150?img=1',
createdAt: new Date()
},
{
name: 'Jane Doe',
email: 'jane@example.com',
password: 'hashed_password',
avatar: 'https://i.pravatar.cc/150?img=2',
createdAt: new Date()
}
]
await db.insert(schema.users).values(users)
return { result: 'Database seeded successfully' }
}
})
Execute the task
Open the Tasks tab in Nuxt DevTools and click on the db:seed task.
CLI
NuxtHub provides a CLI for managing your database migrations and running SQL queries accessible from the npx nuxt db command.
nuxt db generate
Generate database migrations from the schema.
USAGE db generate [OPTIONS]
OPTIONS
--cwd The directory to run the command in.
-v, --verbose Show verbose output.
nuxt db migrate
Apply database migrations to the database.
USAGE db migrate [OPTIONS]
OPTIONS
--cwd The directory to run the command in.
--dotenv Point to another .env file to load.
-v, --verbose Show verbose output.
nuxt db mark-as-migrated
Mark local database migration(s) as applied to the database.
USAGE db mark-as-migrated [OPTIONS] [NAME]
ARGUMENTS
NAME The name of the migration to mark as applied.
OPTIONS
--cwd The directory to run the command in.
--dotenv Point to another .env file to load.
-v, --verbose Show verbose output.
nuxt db drop
Drop a table from the database.
USAGE db drop [OPTIONS] <TABLE>
ARGUMENTS
TABLE The name of the table to drop.
OPTIONS
--cwd The directory to run the command in.
--dotenv Point to another .env file to load.
-v, --verbose Show verbose output.
nuxt db sql
Execute a SQL query against the database.
USAGE db sql [OPTIONS] [QUERY]
ARGUMENTS
QUERY The SQL query to execute. If not provided, reads from stdin.
OPTIONS
--cwd The directory to run the command in.
--dotenv Point to another .env file to load, relative to the root directory.
-v, --verbose Show verbose output.
Example usage:
npx nuxt db sql "SELECT * FROM users"
# or
npx nuxt db sql < dump.sql
AI Agents
If you work with an IDE that supports AI agents, you can add the following text in your Agents.md or .cursor/rules file:
# Agent Instructions
/** ... your agent instructions ... */
## Database
- **Database Dialect**: The database dialect is set in the `nuxt.config.ts` file, within the `hub.db` option or `hub.db.dialect` property.
- **Drizzle Config**: Don't generate the `drizzle.config.ts` file manually, it is generated automatically by NuxtHub.
- **Generate Migrations**: Use `npx nuxt db generate` to automatically generate database migrations from schema changes
- **Never Write Manual Migrations**: Do not manually create SQL migration files in the `server/db/migrations/` directory
- **Workflow**:
1. Create or modify the database schema in `server/db/schema.ts` or any other schema file in the `server/db/schema/` directory
2. Run `npx nuxt db generate` to generate the migration
3. Run `npx nuxt db migrate` to apply the migration to the database, or run `npx nuxt dev` to apply the migration during development
- **Access the database**: Use the `db` instance from `hub:db` to query the database, it is a Drizzle ORM instance.
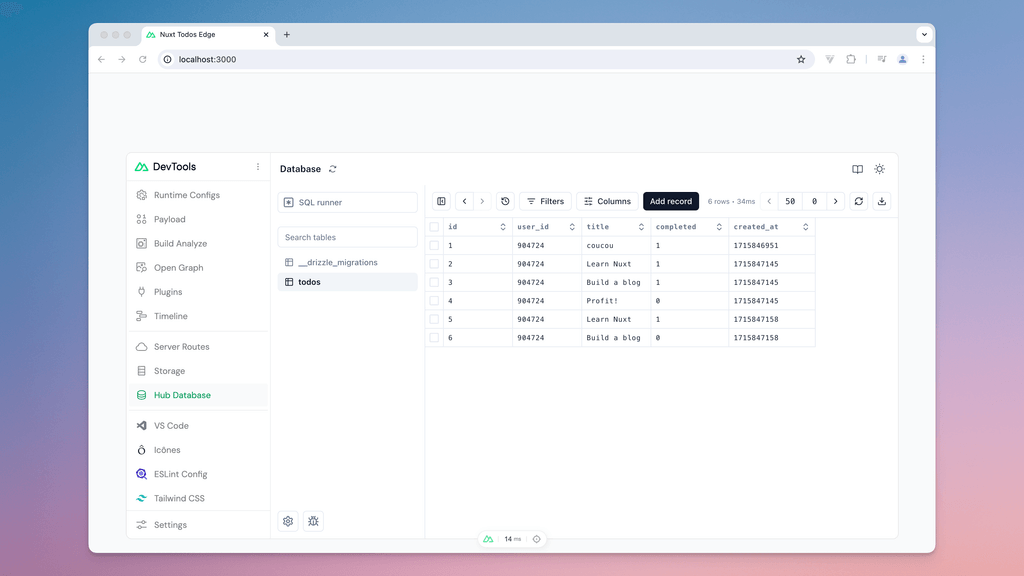
Local development
During local development, view and edit your database from Nuxt DevTools using the Drizzle Studio:
Build-time Hooks
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hooks: {
'hub:db:migrations:dirs': (dirs) => {
dirs.push('my-module/db/migrations')
}
}
})
_hub_migrations table which are applied after the database migrations complete.export default defineNuxtConfig({
hooks: {
'hub:db:queries:paths': (queries, dialect) => {
queries.push('my-module/db/queries')
}
}
})
import { createResolver, defineNuxtModule } from '@nuxt/kit'
export default defineNuxtModule({
setup(options, nuxt) {
const { resolve } = createResolver(import.meta.url)
nuxt.hook('hub:db:schema:extend', ({ paths, dialect }) => {
paths.push(resolve(`./db/schema/pages.${dialect}.ts`))
})
}
})
Advanced configuration
For advanced use cases, you can explicitly configure the database connection:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
db: {
dialect: 'postgresql',
driver: 'postgres-js', // Optional: explicitly choose driver
connection: {
connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL
}
}
}
})
Cloudflare D1 over HTTP
Use the d1-http driver to access a Cloudflare D1 database over HTTP. This is useful when you want to query your D1 database when hosting on other platforms.
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
db: {
dialect: 'sqlite',
driver: 'd1-http'
}
}
})
This driver requires the following environment variables:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
NUXT_HUB_CLOUDFLARE_ACCOUNT_ID | Your Cloudflare account ID |
NUXT_HUB_CLOUDFLARE_API_TOKEN | A Cloudflare API token with D1 permissions |
NUXT_HUB_CLOUDFLARE_DATABASE_ID | The ID of your D1 database |
D1:Edit permissions.Migration guide
hubDatabase(), follow this migration guide.Configuration changes
The database option has been renamed to db and now accepts a SQL dialect instead of a boolean.
export default defineNuxtConfig({
hub: {
- database: true
+ db: 'sqlite'
}
})
Valid dialects are sqlite, postgresql and mysql.
Directory changes
The database directory has been renamed from server/database/ to server/db/:
- server/database/schema.ts
+ server/db/schema.ts
- server/database/migrations/
+ server/db/migrations/
Make sure to move your schema and migration files to the new location.
API changes
The old hubDatabase() function has been removed. You must now use Drizzle ORM.
Before:
const db = hubDatabase()
const result = await db.prepare('SELECT * FROM users').all()
After:
const result = await db.select().from(tables.users)
Migration files
Your existing SQL migration files continue to work! Just move them to server/db/migrations/.